Onpage SEO refers to the process of optimizing various elements on the pages of a website in an effort to improve that website’s rank in search engines. Onpage SEO, also known as Technical SEO, includes optimizing each page’s title, description, URL, body text and several more. An often overlooked aspect of onpage optimization are the images used on the website.
People add images to a website mostly for aesthetic or visual reasons. They are often completely unaware of the images’ properties that relate to search engine optimization.
In addition to helping improve a website’s rank, optimizing images can also lead to a better user experience. After all, websites should be built with people in mind, and every effort should be taken to maximize the user experience.
Why image optimization is important
Search engines like Google, scour the internet looking for web pages to index. When they find a website, search engines will parse the content of each page to figure out what the page is about.
Essentially search engines are trying to rank a web page for the keywords people will be entering as search terms to find the information they are looking for.
Every element on the web page is an opportunity to help search engines understand what the page is about, and ultimately help improve its relevancy and rank.
Search engines will examine various elements on the web page including the page title, URL, links embedded on the page, and page text. Unfortunately, images can not be parsed by search engines; however, there are some attributes of an image that we can use to tell a search engine what the image is about.
So how are images optimized for better user experience and improved SEO? There are several easy tricks to keep in mind when adding images to your website.
To help illustrate the image optimization techniques used in this article, I will apply the techniques against a random image I downloaded from the internet.
Here’s our sample image:

The following are a few pieces of information from the image to keep in mind as we explore our image optimization techniques:
Original filename: pexels-photo-414630.jpeg
Original image size: 4,800KB
Original dimensions: 5,997pixels wide by 4,000pixels high
Image Size
The process of optimizing an image for SEO starts even before an image is uploaded to the website. The first thing to consider is the size of the image.
Whether you are using a photo downloaded from a stock photography website or using a photo taken with your phone or DSLR camera, chances are the size of the image is much bigger than it needs to be for your website.
Most modern cameras and phones produce high resolution images that are at least 3,000KB – 5,000KB in size or even bigger.
The size of the images you use on your website affects the overall loading speed of the website. Google estimates that nearly half of all visitors will leave a website if the pages don’t load within 3 seconds.
Keeping the image sizes as small as possible will therefore mean you won’t be losing potential customers due to a slow loading website.
As a rule of thumb, you should aim to keep most of the images on your website below 100KB in size.
So how do you go about reducing the size of images you plan to use on your website? It’s quite simply, really. There are many online tools you can use, but one of my favourite tools is ResizeImage.net.
Let’s head over to resizeimage.net now to optimize our sample image.
The interface has lots of options and might be overwhelming for someone using the tool for the first time. But there are only 4 things you need to do:
- Upload the image. This might take a few seconds depending on the size of the image. Wait until your see a preview of the image on the page.

- Once the upload is complete, scroll down to Step 4 in the tool to Resize Your Image. The desired dimensions of your image will depend on what the image is being used for. For example, the size of an image being used as a banner will be different from an image being used in a blog post. But for most purposes, the width of the image doesn’t need to exceed 800 pixels. So go ahead and change the width to 800px. Make sure to keep the “Keep Aspect Ratio” flag checked.

Note: The dimensions of your images will ultimately depend on the design of your website and how the images will be used. You might need to experiment with different dimensions if you find 800px either to be too big or too small.
- Now scroll down to Step 7 to optimize the “quality” of the image. Select Progressive compression and set the Image Quality to 80%. The lower the Image Quality value the smaller the size of the resized image. However, going too low will also reduce the visual quality of the image, making the image appear blurry or pixelated. Again, experiment with different values to get the right balance between quality and image size.

- Click the Resize button to resize and compress the image in one step. Wait for the tool to do its thing and take a look at the results. In my example, I was able to reduce the image size down to 48.7KB! That’s a reduction of about 99%!
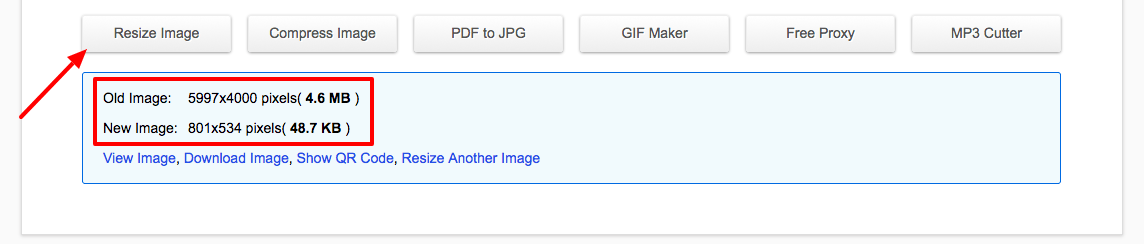
Image Filename
When you take a photograph using your phone or DSLR camera, or download a stock photo to use on your website, do you usually look at at the filename of the image?
A photograph taken with a phone or camera will typically look as follows: IMG_20170912_224752.jpg.
When you upload the image to your website, the filename becomes part of the URL:
https://nubranch.ca/images/IMG_20170912_224752.jpg
When search engines come across an image on your web page, they will parse the filename in an effort to identify what the image is about.
Keeping the default filename given to an image by a camera or stock photography sites will not help search engines understand what the image is about.
Changing the filename to something more descriptive helps search engines paint a clearer picture of what the image is about.
But what do you change the image filename to?
Well, that depends on the image itself and also the topic of your page. Let’s go back to our sample image to take a closer look.
The original filename is pexels-photo-414630.jpeg.
The URL of the image will be: https://nubranch.ca/images/pexels-photo-414630.jpeg
This doesn’t tell search engines anything useful. A more informative filename should include words that describe the image. One such filename could be coffee-cup-laptop.jpeg.
Some important naming conventions to keep in mind when renaming files:
- Keep the filename short and descriptive.
- Use dashes to separate the words to make it easier for search engines to parse the filename.
- Avoid using stop words – these are words like “a” and “the”.
- Start the filename with the more important keywords. For example, if our article was about office culture, a more appropriate filename might be office-culture-coffee-cup.jpeg.
Alt Text
The Alt text, short for Alternative text, is an HTML attribute of the image tag. The Alt text serves as a way to provide a short description of the image. Since Google can’t “read” an image, the Alt text provides Google with useful information about the subject matter of the image.
Additionally, special software used by the visually impaired relies on the content of Alt text to describe the images on a website. So there is a user experience element to the Alt text.
Another important consideration when generating the content of the Alt text is to make sure you include keywords you are trying to rank your page for. Including important keywords in the Alt text of an image can help search engines understand its relevance.
Consider these simple examples using our coffee image:
No Good:
<img src="coffee-cup" alt="" />
Better:
<img src="coffee-cup" alt="coffee" />
Best:
<img src="coffee-cup" alt="drinking cup of coffee at work" />
As you can see, an effective Alt text is one that paints a picture of what the image is depicting. A good way to come up with effective content for the Alt text is to ask yourself: How would I describe this image to someone who can’t see it?
You might be wondering at this point how one goes about adding the Alt text to images on their website. Well, that really depends on the platform you are using for your website. The good news is that most platforms, like WordPress, Joomla, Wix and others, provide an easy-to-use interface for typing in the Alt text.
Since WordPress is the most popular platform, I’m going to use WordPress to illustrate how you would add the Alt text to your images.
Log in to your website’s admin area, and then head over to the Media Library area:

Next click on the image you wish to add the Alt Text to. Scroll down and locate the “Alternative Text” field. Add your text in the space provided, and then hit the Update button. Done!

Bonus: Logo Image Optimization
A company logo is an image that is found on pretty much every business website out there. Typically appearing in the header, it’s the first image a search engine will encounter on a website.
A properly optimized logo image is an opportunity to tell search engines what a website is about, and so the logo requires some special attention.
Surprisingly though, the logo is often the least SEO optimized image on a website.
That’s probably because the logo is added to a website when the website is first designed, way before optimization is part of the business’s SEO strategy.
Most logo files are named logo.png. Naturally, right? Although one could argue this filename is short and descriptive, it doesn’t really tell search engines what the website is about.
Here’s what the a typical IMG tag for a logo looks like:
<img src="logo.png" alt="" />
The filename has been kept as the standard “logo.png” name and the Alt text was left empty.
So how do we optimize the logo image? Let’s put into action some of the image hacks we learned so far.
1) Logo Filename
Let’s take the logo of the nuBranch website to illustrate a better way to name a logo image:
<img src="/images/nubranch-web-design-local-seo-logo.png" />
Adding the main business activities to the filename can help provide a strong signal to a search engine about what the site is about.
2) Logo Alt Text
As we discussed earlier, the Alternative Text is an attribute of the IMG tag that is meant to provide a textual description of the image. It’s also an opportunity to include important keywords we want our website to rank for, including the location of the business.
Looking at the nuBranch website again, let’s examine the ALT text of the logo image:
<img src="/images/nubranch-web-design-local-seo-logo.png" alt="Web Design & Local SEO, Toronto" />
Just like the filename, the Alt text sends a strong signal to search engines, helping them understand what the website is about.
Wrapping Up
Image SEO hacks are often overlooked when it comes to optimizing a website or a blog post. The optimization areas outlined in this article include:
- Image Size: keep it under 100KB
- Image Filename: keep it short and descriptive
- Alternative Text attribute: remember to include your keywords
Performing these simple image optimization techniques only takes a few seconds, but can result in boosting your search engine rankings, and can give you the competitive edge to outrank your competition!





